In the Philippines, regions (Tagalog: rehiyon, ISO 3166-2:PH) are administrative divisions that serve primarily to organize the provinces (lalawigan) of the country for administrative convenience. Currently, the archipelagic republic of the Philippines is divided into 17 regions. Most government offices are established by region instead of individual provincial offices, usually (but not always) in the city designated as the regional center.
The regions themselves do not possess a separate local government, with the exception of the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, which has an elected regional assembly and governor. The Cordillera Administrative Region was originally intended to be autonomous (Cordillera Autonomous Region), but the failure of two plebiscites for its establishment reduced it to a regular administrative region.
History
Regions first came to existence in on September 24, 1972 when the provinces of the Philippines were organized into 11 regions by Presidential Decree No. 1 as part of the Integrated Reorganization Plan of President Ferdinand Marcos.
Since that time, other regions have been created and some provinces have been transferred from one region to another.
- July 7, 1975: Region XII created and minor reorganization of some Mindanao regions.
- August 21, 1975: Region IX divided into Sub-Region IX-A' and Sub-Region IX-B. Minor reorganization of some Mindanao regions.
- November 7, 1975: National Capital Region created.
- August 1, 1989: Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao created.
- October 23, 1989: Cordillera Administrative Region created.
- October 12, 1990: Executive Order issued to reorganize the Mindanao regions but the reorganization never happened (possibly due to lack of government funds).
- February 23, 1995: Region XIII (Caraga) created and minor reorganization of some Mindanao regions.
- 1997: Minor reorganization of some Mindanao regions.
- September 19, 2001: Most Mindanao regions reorganized and some renamed.
- May 17, 2002: Region IV-A (CALABARZON) and Region IV-B (MIMAROPA) created from the former Region IV (Southern Tagalog) region.
- May 23, 2005: Palawan transferred from MIMAROPA to Western Visayas; MIMAROPA renamed to MIMARO.
- August 19, 2005: The E.O. 429 of May 23, 2005 transferring Palawan from MIMAROPA to Western Visayas was later held in abeyance by Administrative Order #129.
As of June 2010, the Philippines consists of 17 administrative regions. Some of the region designations include numeric components, some do not.[1] These regions are geographically combined into the three island groups of Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. Following is a list of the regions in their island groupings. To get overviews of the regions, see the respective articles on the island groups. The regions CALABARZON, MIMAROPA, and SOCCSKSARGEN are capitalized because they are acronyms that stand for their component provinces or cities.[2]
Note that insofar as the Judiciary is concerned, specifically the first and second level courts, the country is divided into judicial regions as provided by Batas Pambansa Bilang 129. The coverage of these judicial regions generally coincides with that of the administrative regions in the Executive branch of government.
Luzon
| Map | Region (short name) | Regional center | Component local government units |
|---|---|---|---|
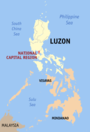 | National Capital Region (NCR; Metro Manila) | Manila |
|
 | Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) | Baguio City |
|
 | Ilocos Region (Region I) | San Fernando City, La Union |
|
 | Cagayan Valley (Region II) | Tuguegarao City |
|
 | Central Luzon (Region III) | San Fernando City, Pampanga |
|
 | CALABARZON (Region IV-A) | Calamba City, Laguna |
|
 | MIMAROPA (Region IV-B) | Calapan City |
|
 | Bicol Region (Region V) | Legazpi City |
|
Visayas
| Map | Region (short name) | Regional center | Component local government units |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Western Visayas (Region VI) | Iloilo City |
|
 | Central Visayas (Region VII) | Cebu City | |
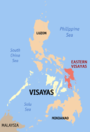 | Eastern Visayas (Region VIII) | Tacloban |
Mindanao
| Map | Region (short name) | Regional center | Component local government units |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Zamboanga Peninsula (Region IX) | Zamboanga City | |
 | Northern Mindanao (Region X) | Cagayan de Oro | |
 | Davao Region (Region XI) | Davao City | |
 | SOCCSKSARGEN (Region XII) | Koronadal | |
 | Caraga Region (Region XIII) | Butuan | |
 | Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) | Cotabato City |
|



